|

In
the case we are following where a man was convicted of rape
of a young girl, apart from the fact that the girl was "tightly
closed", there was also no signs of tearing of the fourchette, or
other trauma associated with digital penetration (without foreplay = dry).
The girl claimed regular assaults of this type that would have produced
scars and the like in 83% of cases, but there were no scars, a finding
which is clearly inconsistent with her claims.
A
partial notch was found in the hymen, but it is now known that such
findings are normal. Tears and the like in the hymen are full width if
caused by trauma, leaving scar tissue, rather than partial (a smooth small
indentation) as in naturally occurring
features. This was not explained to the jury, who were left believing that
there was no explanation for the 'notch' other than penetrative sex, when
in fact it was a naturally occurring feature in all females of all ages.
Yet, an innocent man was sent to prison by the system. In this case the
so-called expert used her position of trust to mislead the Jury, by way of
helping the police to gain a conviction
of a dissident resident who was making waves as to this force failing
to investigate crime in Wealden
District Council. One way of neutralising political opponents is to
discredit them with a sexual allegation. After
that, nobody is likely to believe anything they say.
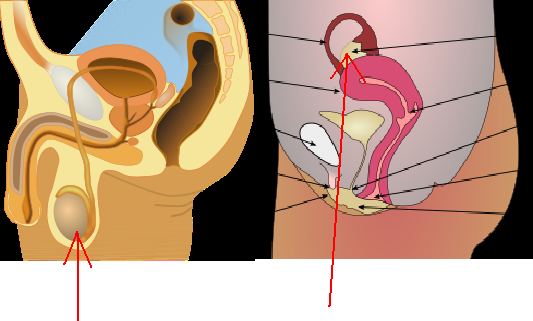
The vulva (derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the vaginal opening, and Bartholin's and Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part of the perineum), and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support.
Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Afferent lymph vessels carry lymph away from the vulva to the inguinal lymph nodes. The nerves that supply the vulva are the pudendal nerve, perineal nerve, ilioinguinal nerve and their branches. Blood and nerve supply to the vulva contribute to the stages of sexual arousal that are helpful in the reproduction process.
Following the development of the vulva, changes take place at birth, childhood, puberty, menopause and post-menopause. There is a great deal of variation in the appearance of the vulva particularly in relation to the labia minora. The vulva can be affected by many disorders which may often result in irritation. Vulvovaginal health measures can prevent many of these. Other disorders include a number of infections and cancers. There are several vulval restorative surgeries known as genitoplasties, and some of these are also used as cosmetic surgery procedures.
Different cultures have held different views of the vulva. Some ancient religions and societies have worshipped the vulva and revered the female as a goddess. Major traditions in Hinduism continue this. In western societies there has been a largely negative attitude typified by the medical terminology of pudenda membra, meaning parts to be ashamed of. There has been an artistic reaction to this in various attempts to bring about a more positive and natural outlook, such as work from British, American, and Japanese artists. While the vagina is a separate part of the anatomy, it has often been used synonymously with vulva.
LABIA
The labia majora and the labia minora cover the vulval vestibule. The outer pair of folds, divided by the pudendal cleft, are the labia majora, (New Latin for "larger lips"). They contain and protect the other structures of the vulva. The labia majora meet at the front at the mons pubis, and meet posteriorly at the urogenital triangle (the anterior part of the perineum) between the pudendal cleft and the anus. The labia minora are often pink or brownish black, relevant to the person's skin color.
The grooves between the labia majora and labia minora are called the interlabial sulci, or interlabial folds. The labia minora (smaller lips) are the inner two soft folds, within the labia majora. They have more color than the labia majora and contain numerous sebaceous glands. They meet posteriorly at the frenulum of the labia minora, a fold of restrictive tissue. The labia minora meet again at the front of the vulva to form the clitoral hood, also known as the prepuce.
The visible portion of the clitoris is the clitoral glans. Typically, this is roughly the size and shape of a pea, and can vary in size from about 6 mm to 25 mm. The size can also vary when it is erect. The clitoral glans contains as many nerve endings as the much larger homologous glans penis in the male, which makes it highly sensitive. The only known function of the clitoris is to focus sexual feelings. The clitoral hood is a protective fold of skin which varies in shape and size, and it may partially or completely cover the clitoris. The clitoris is the homologue of the penis, and the clitoral hood is the female equivalent of the male foreskin, and may be partially or completely hidden within the pudendal cleft.
CLITORIS
The clitoris is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion - the glans - is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the opening of the urethra. Unlike the penis, the male homologue (equivalent) to the clitoris, it usually does not contain the distal portion (or opening) of the urethra and is therefore not used for urination. The clitoris also usually lacks a reproductive function. While few animals urinate through the clitoris or use it reproductively, the spotted hyena, which has an especially large clitoris, urinates, mates, and gives birth via the organ. Some other mammals, such as lemurs and spider monkeys, also have a large clitoris.
The clitoris is the human female's most sensitive erogenous zone and generally the primary anatomical source of human female sexual pleasure. In humans and other mammals, it develops from an outgrowth in the embryo called the genital tubercle. Initially undifferentiated, the tubercle develops into either a penis or a clitoris, depending on the presence or absence of the protein tdf, which is codified by a single gene on the Y chromosome. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The glans (head) of the human clitoris is roughly the size and shape of a pea, and is estimated to have about 8,000 sensory nerve endings.
Sexological, medical, and psychological debate have focused on the clitoris, and it has been subject to social constructionist analyses and studies. Such discussions range from anatomical accuracy, gender inequality, female genital mutilation, and orgasmic factors and their physiological explanation for the G-spot. Although, in humans, the only known purpose of the clitoris is to provide sexual pleasure, whether the clitoris is vestigial, an adaptation, or serves a reproductive function has been debated. Social perceptions of the clitoris include the significance of its role in female sexual pleasure, assumptions about its true size and depth, and varying beliefs regarding genital modification such as clitoris enlargement, clitoris piercing and clitoridectomy. Genital modification may be for aesthetic, medical or cultural reasons.
Knowledge of the clitoris is significantly impacted by cultural perceptions of the organ. Studies suggest that knowledge of its existence and anatomy is scant in comparison with that of other sexual organs, and that more education about it could help alleviate social stigmas associated with the female body and female sexual pleasure; for example, that the clitoris and vulva in general are visually unappealing, that female masturbation is taboo, or that men should be expected to master and control women's orgasms.
SEXUAL AROUSAL
The clitoris and the labia minora are both erogenous areas in the vulva. Local stimulation can involve the clitoris, vagina and other perineal regions. The clitoris is the most sensitive. Sexual stimulation of the clitoris (by a number of means) can result in widespread sexual arousal, and if maintained can result in an orgasm. Stimulation to orgasm is optimally achieved by a massaging sensation.
Sexual arousal results in a number of physical changes in the vulva. During arousal vaginal lubrication increases. Vulva tissue is highly vascularised; arterioles dilate in response to sexual arousal and the smaller veins will compress after arousal, so that the clitoris and labia minora increase in size. Increased vasocongestion in the vagina causes it to swell, decreasing the size of the vaginal opening by about 30%. The clitoris becomes increasingly erect, and the glans moves towards the pubic bone, becoming concealed by the hood. The labia minora increase considerably in thickness. The labia minora sometimes change considerably in color, going from pink to red in lighter skinned women who have not borne a child, or red to dark red in those that have. Immediately prior to an orgasm, the clitoris becomes exceptionally engorged, causing the glans to appear to retract into the clitoral hood. Rhythmic muscle contractions occur in the outer third of the vagina, as well as the uterus and anus. Contractions become less intense and more randomly spaced as the orgasm continues. The number of contractions that accompany an orgasm vary depending on its intensity. An orgasm may be accompanied by female ejaculation, causing liquid from either the Skene's gland or bladder to be expelled through the urethra. The pooled blood begins to dissipate, although at a much slower rate if an orgasm has not occurred. The vagina and vaginal opening return to their normal relaxed state, and the rest of the vulva returns to its normal size, position and color.
GENITAL MUTILATION
In some cultural practices, particularly in the African Khoikhoi and Rwanda cultures, the labia minora are purposefully stretched by repeated pulling on them and sometimes by using attached weights. Labia stretching is a recognised, familial cultural practice in parts of Eastern and Southern Africa. This is a desired and encouraged practice by the women (starting at puberty) in order to promote better sexual satisfaction for both parties. The achieved extensions can hang down below the labia majora for up to seven inches.
In some cultures, including modern Western culture, women have shaved or otherwise removed the hair from part or all of the vulva. When high-cut swimsuits became fashionable, women who wished to wear them would remove the hair on either side of their pubic triangles, to avoid exhibiting pubic hair. Other women relish the beauty of seeing their vulva with hair, or completely hairless, and find one or the other more comfortable. The removal of hair from the vulva is a fairly recent phenomenon in the United States, Canada, and Western Europe, usually in the form of bikini waxing or Brazilian waxing, but has been prevalent in many Eastern European and Middle Eastern cultures for centuries, usually due to the idea that it may be more hygienic, or originating in prostitution and pornography. Hair removal may include all, most, or some of the hair. French waxing leaves a small amount of hair on either side of the labia or a strip directly above and in line with the pudendal cleft called a landing strip. Islam teaching includes Muslim hygienical jurisprudence a practice of which is the removal of pubic hair.
Several forms of genital piercings can be made in the female genital area, and include the Christina piercing, the Nefertiti piercing, the fourchette piercing, and labia piercings. Piercings are usually performed for aesthetic purposes, but some forms like the clitoral hood piercing might also enhance pleasure during sex. Though they are common in traditional cultures, intimate piercings are a fairly recent trend in Western society.
Female genital surgery includes laser resurfacing of the labia to remove wrinkles, labiaplasty (reducing the size of the labia) and vaginoplasty. In September 2007, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) issued a committee opinion on these and other female genital surgeries, including "vaginal rejuvenation", "designer vaginoplasty", "revirgination", and "G-spot amplification". This opinion states that the safety of these procedures has not been documented. The ACOG and the ISSVD recommend that women seeking these surgeries need to be informed about the lack of data supporting these procedures and the potential associated risks such as infection, altered sensation, dyspareunia, adhesions, and scarring.
With the growing popularity of female cosmetic genital surgeries, the practice increasingly draws criticism from an opposition movement of cyberfeminist activist groups and platforms, called the labia pride movement. The major point of contention is that heavy advertising for these procedures, in combination with a lack of public education, fosters body insecurities in women with larger labia in spite of the fact that there is normal and pronounced individual variation in the size of labia. The preference for smaller labia is a matter of a fashion fad and is without clinical or functional significance.
The most prevalent form of non-consensual genital alteration is that of female genital mutilation. This mostly involves the partial or complete removal of genital organs. Female genital mutilation is carried out in thirty countries in Africa, and Asia with more than 200 million girls being affected, and some women (as of 2018). Nearly all of the procedures are carried out on young girls. The practices are also carried out globally among migrants from these areas. Female genital mutilation is claimed to be mostly carried out for cultural traditional reasons.
VULVAS
FROM 1939 TO 1945
|

Adolf
Hitler
German
Chancellor
|

Herman
Goring
Reichsmarschall
|

Heinrich
Himmler
Reichsführer
|

Joseph
Goebbels
Reich Minister
|

Philipp
Bouhler SS
NSDAP
Aktion T4
|

Dr
Josef Mengele
Physician
Auschwitz
|
|

Martin
Borman
Schutzstaffel
|

Adolph
Eichmann
Holocaust
Architect
|

Rudolf
Hess
Commandant
|

Erwin
Rommel
The
Desert Fox
|

Karl
Donitz
Kriegsmarine
|

Albert
Speer
Nazi
Architect
|
CIVIL
SERVANTS INVESTIGATED FOR POSSIBLE ISSUES 1983 TO 2018
|

Ian
Kay
Assist.
Dist. Plan.
|

Charles
Lant
Chief
Executive
|

Victorio
Scarpa
Solicitor
|

Timothy
Dowsett
Dist.
Secretary
|

Christine
Nuttall
Solicitor
|

David
Phillips
Planning
|
|

Daniel
Goodwin
Chief
Executive
|

J
Douglas Moss
Policy
|

Kelvin
Williams
Dist.
Planning
|

Trevor
Scott
Solicitor
|

David
Whibley
Enforcement
|

Christine
Arnold
Planning
|
|

Chris
Bending
District
Planning
|

Beverley
Boakes
Legal
Secretary
|

Patrick
Coffey
Planning
|

Julian
Black
Planning
|

Ashley
Brown
Dist.
Planning
|

Derek
Holness
Former
CEO
|
Abbott
Trevor - Alcock
Charmain - Ditto - Arnold
Chris (Christine) - Barakchizadeh
Lesley - Paul Barker - Bending
Christopher
Black
Julian - Boakes Beverley - Bradshaw
Clifford - Brigginshaw
Marina - Brown
Ashley - Coffey
Patrick - Douglas
Sheelagh
Dowsett Timothy - Flemming
Mike - Forder Ralph - Garrett
Martyn - Goodwin Daniel
- Henham J - Holness
Derek
Hoy
Thomas - Johnson
Geoff - Kavanagh Geoff - Kay Ian - Kay
I. M.
- Barbara Kingsford - Lant Charles - Mercer
Richard
Mileman Niall - Moon
Craig - Moss Douglas, J. - Nuttall
Christine - Pettigrew Rex - Phillips
David - Scarpa
Victorio - Scott
Trevor
Kevin Stewart - Wakeford
Michael. - Whibley David - White,
George - Williams
Kelvin - Wilson Kenneth - White
Steve
HOME |
AFFORDABLE | CLIMATE
| DEVELOPERS | ECONOMY
| FLOOD | HISTORY
| HOMES LADDER
| MORALS
| POVERTY
| PROPERTY | SLAVERY
| TAXES | SLUMS |
VALUATIONS | WEALTH
|


























